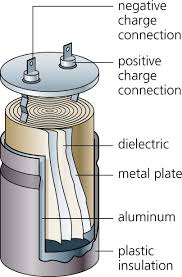
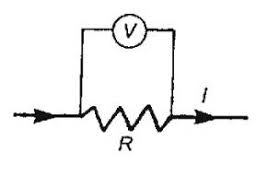
Electric power is defined as the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.
When electric current flows in a circuit, it can transfer energy to do mechanical or thermodynamic work. Devices convert electrical energy into many useful forms, such as heat (electric heaters), light (light bulbs), motion (electric motors), sound (loudspeaker) or chemical changes. Electricity can be produced mechanically by generation, or chemically, or by direct conversion from light in photovoltaic cells, also it can be stored chemically in batteries.
When electric current flows in a circuit, it can transfer energy to do mechanical or thermodynamic work. Devices convert electrical energy into many useful forms, such as heat (electric heaters), light (light bulbs), motion (electric motors), sound (loudspeaker) or chemical changes. Electricity can be produced mechanically by generation, or chemically, or by direct conversion from light in photovoltaic cells, also it can be stored chemically in batteries.